STRATEGIC CONTEXT
Radiological Protection as Strategic Imperative
Radiological Protection
as Strategic Imperative
Geopolitical instability, the expansion of civil nuclear energy, industrial use of radiological materials, and sustained space missions have increased both the likelihood and potential impact of exposure events. Addressing this risk requires scalable, system-level medical countermeasures designed for institutional deployment rather than isolated use cases.
Radiological risk has emerged as a cross-sector challenge affecting public health systems, energy infrastructure, defence readiness, and space operations. Governments and international institutions increasingly recognize that preparedness for radiological exposure cannot rely on fragmented, symptomatic responses.
More than 400 commercial nuclear power reactors are operating worldwide today.
More than 400 commercial nuclear power reactors are operating worldwide today.
More than 12,000 nuclear warheads in global stockpiles, with 9,000+ in military stockpiles for potential use.
More than 12,000 nuclear warheads in global stockpiles, with 9,000+ in military stockpiles for potential use.
Global Scale. The number of medical and industrial radiological facilities is in the tens of thousands globally.
Global Scale. The number of medical and industrial radiological facilities is in the tens of thousands globally.
More than 400 commercial nuclear power reactors are operating worldwide today.
More than 400 commercial nuclear power reactors are operating worldwide today.
More than 12,000 nuclear warheads in global stockpiles, with 9,000+ in military stockpiles for potential use.
More than 12,000 nuclear warheads in global stockpiles, with 9,000+ in military stockpiles for potential use.
Global Scale. The number of medical and industrial radiological facilities is in the tens of thousands globally.
Global Scale. The number of medical and industrial radiological facilities is in the tens of thousands globally.
MISSION
Protecting Lives from Radiation
Protecting Lives from Radiation
USIL Therapeutics addresses a critical capability gap in nuclear and radiological preparedness across defence, civilian, aerospace, and space domains.
Headquartered in Luxembourg, centrally located in Europe, USIL Therapeutics operates within a stable ecosystem spanning EU institutions, aerospace and space activities, and defence coordination, including alignment with NATO procurement frameworks such as the NATO Support and Procurement Agency.
Radiological risk spans civilian and military healthcare, emergency response, energy infrastructure, defence operations, aerospace missions, and space missions. USIL Therapeutics is developing whole-body radioprotective medical countermeasures designed for rapid, institutional deployment in support of European strategic autonomy and health sovereignty.
Our mission is to enable governments, healthcare systems, and allied institutions to protect populations before, during, and after radiological exposure events.
CAPABILITY
CAPABILITY
Dual-Use Radioprotective Medical Countermeasures
Dual-Use Radioprotective
Medical Countermeasures
We develop patented, first-in-class radioprotective compounds intended for broad institutional deployment to protect populations and mission-critical personnel operating within high-risk civilian, industrial, defence, and space environments exposed to ionizing radiation.
These compounds are designed to address both acute, high-dose radiation exposure, including scenarios leading to acute radiation syndrome with hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, and multi-organ injury, as well as prolonged, lower-dose radiation exposure encountered in environments such as space missions.
€10M+ Assets
USIL Therapeutics' asset base comprises a portfolio of multiple patents covering a radioprotective molecule engineered to become a first-in-class medical countermeasure, with protection across the European Union, the United States, and Japan. The platform is supported by validated radiobiology research and regulatory pathways designed for civilian health use, emergency response, and long-term preparedness.
USIL Therapeutics' asset base comprises a portfolio of multiple patents covering a radioprotective molecule engineered to become a first-in-class medical countermeasure, with protection across the European Union, the United States, and Japan. The platform is supported by validated radiobiology research and regulatory pathways designed for civilian health use, emergency response, and long-term preparedness.
USIL Therapeutics' asset base comprises a portfolio of multiple patents covering a radioprotective molecule engineered to become a first-in-class medical countermeasure, with protection across the European Union, the United States, and Japan. The platform is supported by validated radiobiology research and regulatory pathways designed for civilian health use, emergency response, and long-term preparedness.
Global Reach
We collaborate with governments, public institutions, healthcare stakeholders, and defence agencies across Europe and allied regions. By combining advanced science with regulatory and operational alignment, we design radioprotection solutions for deployment in defence field operations, hospitals, emergency response systems, and critical infrastructure. This dual use orientation enables broad adoption while preserving operational credibility.
We collaborate with governments, public institutions, healthcare stakeholders, and defence agencies across Europe and allied regions. By combining advanced science with regulatory and operational alignment, we design radioprotection solutions for deployment in defence field operations, hospitals, emergency response systems, and critical infrastructure. This dual use orientation enables broad adoption while preserving operational credibility.
We collaborate with governments, public institutions, healthcare stakeholders, and defence agencies across Europe and allied regions. By combining advanced science with regulatory and operational alignment, we design radioprotection solutions for deployment in defence field operations, hospitals, emergency response systems, and critical infrastructure. This dual use orientation enables broad adoption while preserving operational credibility.
10+ Experts
USIL Therapeutics integrates senior expertise across radiobiology, drug development, regulatory pathways, institutional preparedness programs, and large-scale manufacturing. Supported by senior scientific, regulatory, and former high-level public-sector advisors, the company is structured to move research through approval and into operationally deployable medical countermeasures across civilian and defence contexts.
USIL Therapeutics integrates senior expertise across radiobiology, drug development, regulatory pathways, institutional preparedness programs, and large-scale manufacturing. Supported by senior scientific, regulatory, and former high-level public-sector advisors, the company is structured to move research through approval and into operationally deployable medical countermeasures across civilian and defence contexts.
USIL Therapeutics integrates senior expertise across radiobiology, drug development, regulatory pathways, institutional preparedness programs, and large-scale manufacturing. Supported by senior scientific, regulatory, and former high-level public-sector advisors, the company is structured to move research through approval and into operationally deployable medical countermeasures across civilian and defence contexts.
DEVELOPMENT PIPELINE
Two Complementary Formulations for Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Two Complementary
Formulations for Acute and Sustained Radiological Exposure
We are advancing two complementary formulations designed to address the distinct phases of ARS, spanning immediate response, hospital-based treatment, and post-event care across field deployment and clinical settings.

/
Acute Response
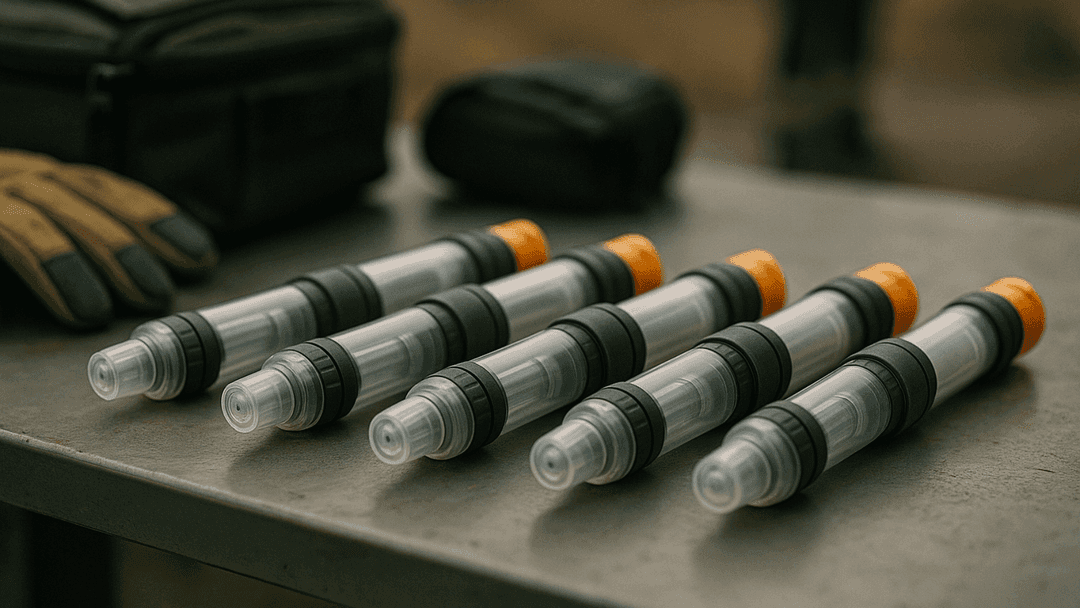
UT-241: IM Auto-Injector
UT-241: IM Auto-Injector
UT-241: IM Auto-Injector
RAPID-RESPONSE RADIATION COUNTERMEASURE
UT-241 is a ready-to-use integral drug–device combination comprising an auto-injector designed for rapid intramuscular administration. Intended for time-critical scenarios involving first responders and exposed populations, it enables rapid deployment in emergency response, industrial incidents, civil protection, and defence operations where speed, portability, and ease of use are essential.
UT-241 is a ready-to-use integral drug–device combination comprising an auto-injector designed for rapid intramuscular administration. Intended for time-critical scenarios involving first responders and exposed populations, it enables rapid deployment in emergency response, industrial incidents, civil protection, and defence operations where speed, portability, and ease of use are essential.


/
PROLONGED COVERAGE
UT-242: IV Infusion
UT-242: IV Infusion
UT-242: IV Infusion
POST-EVENT RADIATION COUNTERMEASURE
UT-242 is an intravenous formulation intended for use in hospitals, field clinics, and specialized treatment centers. It provides extended whole-body radiomitigation across major organ systems and is designed to support prolonged therapeutic coverage following radiation exposure.
UT-242 is an intravenous formulation intended for use in hospitals, field clinics, and specialized treatment centers. It provides extended whole-body radiomitigation across major organ systems and is designed to support prolonged therapeutic coverage following radiation exposure.





/
INTEGRATED RESPONSE
Integrated Whole-Body ARS Coverage
Integrated Whole-Body ARS Coverage
Integrated Whole-Body ARS Coverage
UT-241 and UT-242 are complementary formulations addressing the distinct phases of Acute Radiation Syndrome. UT-241 is intended for immediate response, while UT-242 provides prolonged therapeutic coverage to support post-event mitigation.
UT-241 and UT-242 are complementary formulations addressing the distinct phases of Acute Radiation Syndrome. UT-241 is intended for immediate response, while UT-242 provides prolonged therapeutic coverage to support post-event mitigation.
Advancing Full-Body Radioprotection Beyond Earth
USIL Therapeutics has been selected by the European Space Agency for an in-orbit validation mission aboard the
International Space Station, conducted in partnership with YURI. The study evaluates USIL Therapeutics' whole-body radioprotection approach under microgravity and elevated cosmic radiation to assess stability, biological response, and performance in space-relevant conditions.
Funded by ESA, the project supports dual-use development across spaceflight, defence, and civilian preparedness. Data generated in orbit will inform terrestrial deployment strategies, contributing to the development of field-ready medical countermeasures for astronauts, emergency responders, and other populations exposed to sustained radiation risk.
USIL Therapeutics has been selected by the European Space Agency for an in-orbit validation mission aboard the International Space Station, conducted in partnership with YURI. The study evaluates USIL Therapeutics' whole-body radioprotection approach under microgravity and elevated cosmic radiation to assess stability, biological response, and performance in space-relevant conditions.
Funded by ESA, the project supports dual-use development across spaceflight, defence, and civilian preparedness. Data generated in orbit will inform terrestrial deployment strategies, contributing to the development of field-ready medical countermeasures for astronauts, emergency responders, and other populations exposed to sustained radiation risk.
USIL Therapeutics has been selected by the European Space Agency for an in-orbit validation mission aboard the International Space Station, conducted in partnership with YURI. The study evaluates USIL Therapeutics' whole-body radioprotection approach under microgravity and elevated cosmic radiation to assess stability, biological response, and performance in space-relevant conditions.
Funded by ESA, the project supports dual-use development across spaceflight, defence, and civilian preparedness. Data generated in orbit will inform terrestrial deployment strategies, contributing to the development of field-ready medical countermeasures for astronauts, emergency responders, and other populations exposed to sustained radiation risk.
Institutional Mandates
Institutional Mandates
Institutional Mandates
USIL Therapeutics holds two formal mandates within the European Commission’s Joint Industrial Cooperation Forum (ICF), an industry platform established to support EU preparedness and response capabilities for serious cross-border health threats. The ICF operates under the authority of the European Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA).
Through its participation, USIL Therapeutics contributes to ICF working groups addressing supply-chain resilience and manufacturing readiness, as well as innovation, access, and strategic preparedness for medical countermeasures, supporting the implementation of the EU Medical Countermeasures Strategy.
This mandates USIL Therapeutics' input in strategic EU preparedness discussions and aligns our industry perspective with regulatory and policy development.
USIL Therapeutics holds two formal mandates within the European Commission’s Joint Industrial Cooperation Forum (ICF), an industry platform established to support EU preparedness and response capabilities for serious cross-border health threats. The ICF operates under the authority of the European Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA).
Through its participation, USIL Therapeutics contributes to ICF working groups addressing supply-chain resilience and manufacturing readiness, as well as innovation, access, and strategic preparedness for medical countermeasures, supporting the implementation of the EU Medical Countermeasures Strategy.
This mandates USIL Therapeutics' input in strategic EU preparedness discussions and aligns our industry perspective with regulatory and policy development.
USIL Therapeutics holds two formal mandates within the European Commission’s Joint Industrial Cooperation Forum (ICF), an industry platform established to support EU preparedness and response capabilities for serious cross-border health threats. The ICF operates under the authority of the European Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA).
Through its participation, USIL Therapeutics contributes to ICF working groups addressing supply-chain resilience and manufacturing readiness, as well as innovation, access, and strategic preparedness for medical countermeasures, supporting the implementation of the EU Medical Countermeasures Strategy.
This mandates USIL Therapeutics' input in strategic EU preparedness discussions and aligns our industry perspective with regulatory and policy development.
GOVERNANCE
Leadership & Advisory Board

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.
Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose Morente
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.
GOVERNANCE
Leadership & Advisory Board

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.
GOVERNANCE
Leadership & Advisory Board

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.

Fred Marin
CEO & CO-FOUNDER
Pharm.D. by training, entrepreneur with 20+ years’ experience leading multifunctional, multicultural teams in diverse industries.

Bruno Le Grand
CSO & CO-FOUNDER
PhD, pharmacology and drug development expert with 35 years’ experience in biopharma and healthcare.

Bruno Flamion
CRO & CO-FOUNDER
MD, PhD, former Chair of the Scientific Advice Working Party at the European Medicines Agency (EMA).

Michel Andraud
CFO & CO-FOUNDER
CFO with 30+ years’ experience in finance and M&A across international industrial groups.

Valentin Wiedling
CDO & CO-FOUNDER
Entrepreneur, Harvard-trained, with 15+ years’ experience in investor relations and scaling international ventures.

Catherine Federspiel
HEAD OF STRATEGY
15+ years’ experience in international consulting, aligning strategy and operations to optimize performance.

Jose More
HEAD OF MANUFACTURING
International executive with 25+ years’ experience in automotive with focus on manufacturing.

Alain Rodermann
INVESTMENT ADVISOR
VC leader with 27+ years’ experience, founder of Expon Capital, driving deeptech and innovation across Europe.

Stefan Dimitrov-Lübcke
SPACE ADVISOR
Yuri LUX Managing Director, expert in payloads to Low Earth Orbit with 20+ years in technology regulation and life sciences business development.
PARTNERSHIP
Strategic Partnership Rationale
Strategic Partnership Rationale
Strategic Partnership Rationale
USIL Therapeutics is building a foundational capability for radiological preparedness across defence and civilian frameworks. Delivering this capability at scale requires close collaboration across public institutions, regulators, industrial partners, and operational stakeholders.
With patented assets, validated scientific foundations, and regulatory pathways aligned with healthcare and emergency-use mechanisms, USIL Therapeutics partners with governments, institutions, and long-term stakeholders to enable scalable, dual-use medical countermeasures in a high-impact but historically underprepared risk domain.
Headquartered in Luxembourg, at the intersection of European health, security, and space ecosystems, USIL Therapeutics is positioned for cross-border collaboration, institutional integration, and long-term preparedness at scale.
PARTNERSHIP
LITERATURE
Selected Publications
The following publications illustrate scientific contexts related to radioprotective mechanisms and oxidative stress mitigation.
Hydrogen Sulfide Metabolism and Pulmonary Hypertension
This review highlights the role of hydrogensulfide (H₂S) as a key regulator of vascular remodeling, inflammation, andoxidative stress in pulmonary hypertension (PH). It shows how disrupted H₂Smetabolism affects KATP channel activity and hypoxia responses, identifying H₂S supplementation as a promising antioxidative and vasoprotective therapy.
Inhibition of NF-κB Activation in Human T-Cell Lines by Anetholdithiolthione
This study demonstrates thatanetholdithiolthione (ADT), a pro-glutathione antioxidant, inhibits NF-κBactivation in human T-cells under oxidative and inflammatory stress. ADT reduced lipid peroxidation, boosted glutathione levels, and showed a protective redox-modulating effect, highlighting its potential in HIV and oxidative stress–related disorders.
Targeting Human Lung Adenocarcinoma with a Suppressor of Mitochondrial Superoxide Production
This preclinical study shows that AOL, amitochondrial ROS suppressor (S1QEL), reduces tumor growth in human lung adenocarcinoma by lowering ROS without affecting complex I activity. AOL reprograms cancer metabolism, suppresses the Warburg effect, and modulates NDUFV1, its identified binding site - demonstrating a dual role in REDOX controland cancer signaling.
Effects of OP2113 on Myocardial Infarct Size and No Reflow in a Rat Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Model
This study highlights the cardioprotective effects of OP2113, a mitochondrial ROS–modulating compound, in a ratischemia/reperfusion model. OP2113 reduced mtROS generation, preserved ATPlevels, and significantly lowered infarct size and no-reflow area withoutaffecting hemodynamics, supporting its potential as a mitochondrial-targetedtherapy for myocardial injury.
An old medicine as a new drug to prevent mitochondrial complex I from producing oxygen radicals
This study identifies OP2113 as the first approved drug to selectively inhibit mitochondrial ROS production at the IQ site of complex I without affecting oxidative phosphorylation. In ex vivo ratheart models, it protected cardiac tissue and preserved contractile function, highlighting its potential as a mitochondrial ROS blocker (S1QEL) for neurodegenerative and ischemia-reperfusion disorders.
Hydrogen Sulfide Metabolism and Pulmonary Hypertension
This review highlights the role of hydrogensulfide (H₂S) as a key regulator of vascular remodeling, inflammation, andoxidative stress in pulmonary hypertension (PH). It shows how disrupted H₂Smetabolism affects KATP channel activity and hypoxia responses, identifying H₂S supplementation as a promising antioxidative and vasoprotective therapy.
Inhibition of NF-κB Activation in Human T-Cell Lines by Anetholdithiolthione
This study demonstrates thatanetholdithiolthione (ADT), a pro-glutathione antioxidant, inhibits NF-κBactivation in human T-cells under oxidative and inflammatory stress. ADT reduced lipid peroxidation, boosted glutathione levels, and showed a protective redox-modulating effect, highlighting its potential in HIV and oxidative stress–related disorders.
Targeting Human Lung Adenocarcinoma with a Suppressor of Mitochondrial Superoxide Production
This preclinical study shows that AOL, amitochondrial ROS suppressor (S1QEL), reduces tumor growth in human lung adenocarcinoma by lowering ROS without affecting complex I activity. AOL reprograms cancer metabolism, suppresses the Warburg effect, and modulates NDUFV1, its identified binding site - demonstrating a dual role in REDOX controland cancer signaling.
Effects of OP2113 on Myocardial Infarct Size and No Reflow in a Rat Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Model
This study highlights the cardioprotective effects of OP2113, a mitochondrial ROS–modulating compound, in a ratischemia/reperfusion model. OP2113 reduced mtROS generation, preserved ATPlevels, and significantly lowered infarct size and no-reflow area withoutaffecting hemodynamics, supporting its potential as a mitochondrial-targetedtherapy for myocardial injury.
An old medicine as a new drug to prevent mitochondrial complex I from producing oxygen radicals
This study identifies OP2113 as the first approved drug to selectively inhibit mitochondrial ROS production at the IQ site of complex I without affecting oxidative phosphorylation. In ex vivo ratheart models, it protected cardiac tissue and preserved contractile function, highlighting its potential as a mitochondrial ROS blocker (S1QEL) for neurodegenerative and ischemia-reperfusion disorders.
Hydrogen Sulfide Metabolism and Pulmonary Hypertension
This review highlights the role of hydrogensulfide (H₂S) as a key regulator of vascular remodeling, inflammation, andoxidative stress in pulmonary hypertension (PH). It shows how disrupted H₂Smetabolism affects KATP channel activity and hypoxia responses, identifying H₂S supplementation as a promising antioxidative and vasoprotective therapy.
Inhibition of NF-κB Activation in Human T-Cell Lines by Anetholdithiolthione
This study demonstrates thatanetholdithiolthione (ADT), a pro-glutathione antioxidant, inhibits NF-κBactivation in human T-cells under oxidative and inflammatory stress. ADT reduced lipid peroxidation, boosted glutathione levels, and showed a protective redox-modulating effect, highlighting its potential in HIV and oxidative stress–related disorders.
Targeting Human Lung Adenocarcinoma with a Suppressor of Mitochondrial Superoxide Production
This preclinical study shows that AOL, amitochondrial ROS suppressor (S1QEL), reduces tumor growth in human lung adenocarcinoma by lowering ROS without affecting complex I activity. AOL reprograms cancer metabolism, suppresses the Warburg effect, and modulates NDUFV1, its identified binding site - demonstrating a dual role in REDOX controland cancer signaling.
Effects of OP2113 on Myocardial Infarct Size and No Reflow in a Rat Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Model
This study highlights the cardioprotective effects of OP2113, a mitochondrial ROS–modulating compound, in a ratischemia/reperfusion model. OP2113 reduced mtROS generation, preserved ATPlevels, and significantly lowered infarct size and no-reflow area withoutaffecting hemodynamics, supporting its potential as a mitochondrial-targetedtherapy for myocardial injury.
An old medicine as a new drug to prevent mitochondrial complex I from producing oxygen radicals
This study identifies OP2113 as the first approved drug to selectively inhibit mitochondrial ROS production at the IQ site of complex I without affecting oxidative phosphorylation. In ex vivo ratheart models, it protected cardiac tissue and preserved contractile function, highlighting its potential as a mitochondrial ROS blocker (S1QEL) for neurodegenerative and ischemia-reperfusion disorders.
CONTACT
Get in Touch
Whether you represent a government authority, public institution, industry partner, healthcare organization, or are simply interested in our work, we welcome your inquiry. Please share your details and a brief description of your message below. All communications are handled confidentially.
CONTACT